
This method uses a weight attached to a stranded insulated wire and an ammeter to indicate a closed circuit. Electric sounders are a practical land cost-effective method used to measure well water levels.Acoustic well sounders or echometers are a simple, cost effective, and minimally intrusive tool used to measure subsurface pressures and levels.Transducers are used to measure water levels in groundwater wells, rivers, streams, tanks, open channels and lift stations.Well yield is the volume of water per unit time that is produced by the well from pumping.

Water table is the upper level of the zone of saturation, an underground surface in which the soil or rock is permanently saturated with water.Static level is the level of water in the well when no water is being removed from the well by pumping.Specific capacity is the well yield per unit of drawdown.Pumping level is the level of water in the well during pumping.
#Drawdown definition hydrogeology free
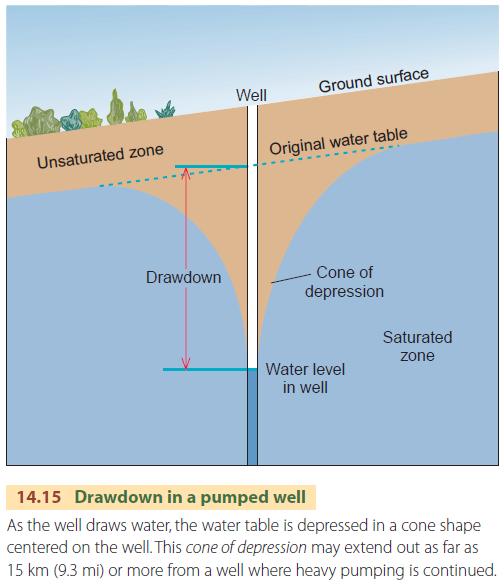
It is the height of the free surface of water above a given point beneath the surface. Hydraulic head (or piezometric head) is a specific measurement of the potential of water above a vertical datum.Groundwater is water located beneath the earth's surface in pores and fractures of soil and rocks.Cone of depression is a conically-shaped depression that is produced in a water table as a result of pumping water from a well at a given rate.Aquifer test (or a pumping test) is a field experiment in which a well is pumped at a controlled rate and the aquifer's response (drawdown) is measured in one or more observation wells.Aquifer is an underground layer of permeable rock or sand, that hold or transmit groundwater below the water table that yield a significant supply of water to a well.regional seasonal decline due to discharge in excess of recharge.in response to local, intensive groundwater pumping.interference from a neighbouring pumping bore.The main contributor to groundwater drawdown since the 1960s is over-exploitation of groundwater resources. A record of hydraulic head, or rate of flow ( discharge), versus time is more generally called a hydrograph (in both groundwater and surface water). Drawdown is often represented in cross-sectional diagrams of aquifers. In either case, drawdown is the change in hydraulic head or water level relative to the initial spatial and temporal conditions of the system.

In layered systems, one also uses constant-head tests to estimate the properties of aquitards (vertical hydraulic conductivity and specific storage).

For the pumped aquifer, one seeks to determine transmissivity, hydraulic conductivity (horizontal and vertical) and storativity (storage coefficient). The goal of a constant-head test, as in any aquifer test, is to estimate hydraulic properties of an aquifer system. Typical well configuration for constant-head test in nonleaky confined aquifer.Ī constant-head test (or constant-drawdown test) is a controlled field experiment in which head (drawdown) in a control well is maintained at a constant level while discharge is monitored through time at the contol well water-level response ( drawdown) may be measured in one or more nearby observation wells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
